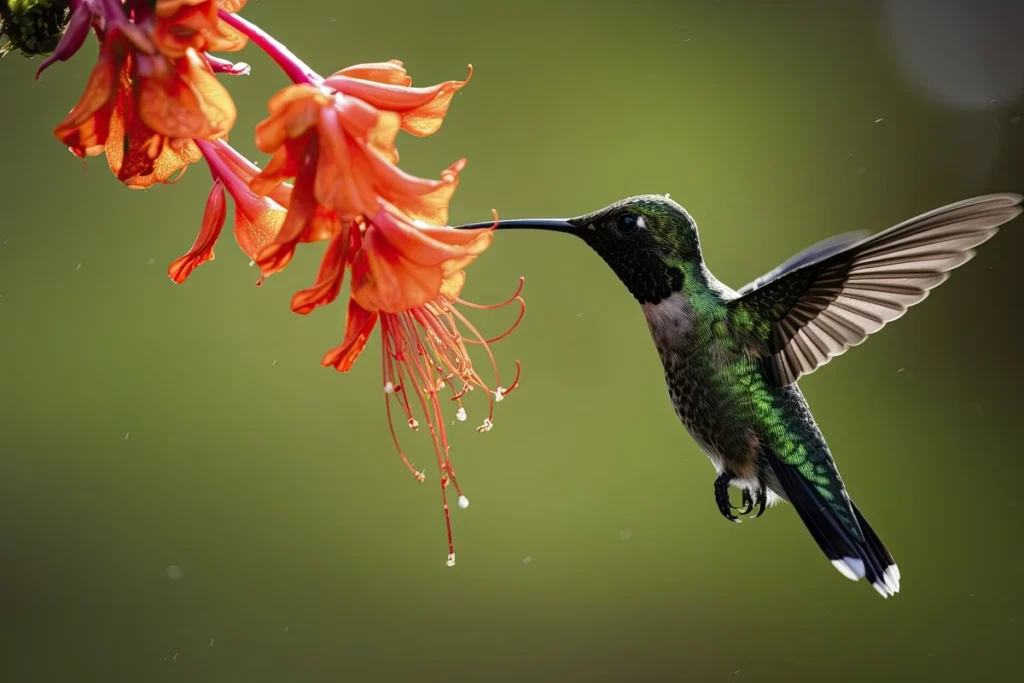
The Bumblebee Hummingbird (Mellisuga helenae) holds the title of the world’s smallest bird, measuring only 2.0 to 2.4 inches in length and weighing between 1.6 to 2.0 grams. These tiny marvels are often overlooked but are truly wonders of nature. Predominantly found in Cuba and the Isla de la Juventud, the Bumblebee Hummingbird captivates bird lovers and casual observers alike with its striking iridescent plumage and incredible flying abilities. This guide explores the unique characteristics of the Bumblebee Hummingbird, focusing on its physical traits, behavior, habitat, and conservation status.
Overview of the Bumblebee Hummingbird
What is the Bumblebee Hummingbird?
As a member of the hummingbird family, the Bumblebee Hummingbird stands out for its small size and vivid colors. It has fascinated ornithologists and bird watchers for years, serving as a testament to the diversity and uniqueness of avian species.
Habitat and Distribution
The Bumblebee Hummingbird thrives in subtropical or tropical forests, scrublands, and grasslands. These habitats are rich in flowering plants, which are vital for their diet. Dense vegetation also provides essential shelter from predators, making these environments ideal for nesting and foraging.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Weight
The Bumblebee Hummingbird is notable for its diminutive size and not like parrots . Adults typically measure between 2.0 and 2.4 inches long, with males usually being smaller than females. Their feather-light weight of just 1.6 to 2.0 grams allows them to flit effortlessly from flower to flower.
Coloration and Plumage
One of the most striking features of the Bumblebee Hummingbird is its vivid iridescent feathers, which change color depending on the angle of light. Males boast emerald green and bright blue plumage, while females exhibit a subtler mix of green and brown. This sexual dimorphism plays a crucial role in mating rituals and helps with camouflage among leaves.
Unique Features
The Bumblebee Hummingbird has several unique adaptations. Its long, slender beak is perfectly designed for extracting nectar from deep-seated flowers. Additionally, its wings can flap at a rate of up to 80 beats per second, allowing for remarkable agility and precision in flight.
Behavior and Feeding Habits
Feeding Techniques
Feeding is a vital aspect of the Bumblebee Hummingbird’s daily routine. These birds primarily consume nectar, which provides the energy required for their high metabolism. They also supplement their diet with insects and spiders for essential protein. Their specialized tongues can extend to efficiently lap up nectar from flowers.
Flight Patterns
The Bumblebee Hummingbird is known for its extraordinary flying abilities. Not only can they hover in mid-air, but they can also fly backward and make sharp turns. These skills are crucial for navigating their environment and accessing food sources that other birds cannot reach. Additionally, these flight patterns play an essential role in their courtship displays during the breeding season.
Social Behavior
While Bumblebee Hummingbirds are generally solitary, they exhibit territorial behavior, especially during mating season. Males may defend their feeding territories against rivals, asserting dominance through aggressive displays. However, outside the breeding season, they can often be seen mingling in areas abundant with flowers.
Reproduction and Nesting
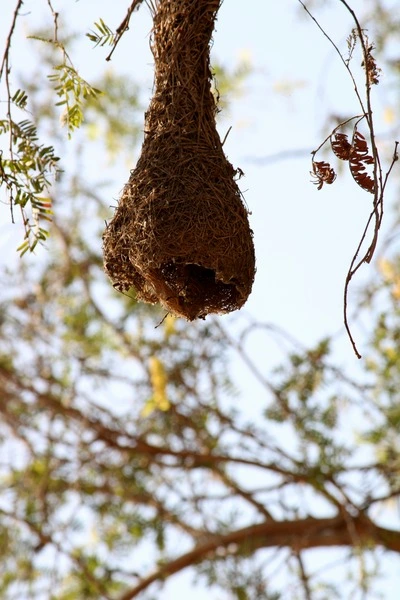

Mating Rituals
Courtship among Bumblebee Hummingbirds is a visually captivating process. Males perform intricate aerial displays to attract females, showcasing their agility and vibrant plumage. These displays often include rapid dives and swoops, making for a stunning spectacle.
Nesting Habits
Once mating is successful, females build nests that are typically camouflaged among leaves or branches. These nests are constructed from plant fibers, spider silk, and feathers, creating a safe environment for their eggs. A female usually lays two tiny eggs, about the size of a pea.
Care of Young
After the eggs hatch, the female takes on the primary caregiving role. She feeds her chicks a diet of regurgitated nectar and small insects, ensuring they receive the necessary nutrients for growth. The young hummingbirds remain in the nest for about three weeks before they are ready to fledge. Care of Hummingbirds at wild care
Conservation Status
Threats to the Bumblebee Hummingbird
Despite their incredible adaptations, Bumblebee Hummingbirds face several threats. Habitat destruction due to agricultural expansion and urban development poses a significant risk to their populations. Additionally, climate change can impact the availability of food sources and nesting sites.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation initiatives are crucial for ensuring the survival of the Bumblebee Hummingbird. Efforts such as reforestation and sustainable agricultural practices aim to protect their natural habitats. Furthermore, raising awareness about the importance of these unique birds can help garner support for conservation efforts.
Fun Facts About the Bumblebee Hummingbird
- Fastest Metabolism: The Bumblebee Hummingbird has one of the fastest metabolisms of any animal, requiring it to consume up to twice its body weight in nectar daily.
- Unique Migration Patterns: Unlike some other hummingbird species, the Bumblebee Hummingbird does not migrate. They are resident birds that remain in their breeding grounds year-round.
- Vocalizations: While generally silent, these birds can produce a range of chirps and whistles, especially during courtship.
Conclusion
The Bumblebee Hummingbird is a remarkable example of nature’s ingenuity. Its unique characteristics—from its small size to its striking plumage—make it a fascinating subject for study and admiration. By understanding and appreciating these tiny birds, we can contribute to their conservation and ensure that future generations can enjoy their beauty.
Call to Action
Have you ever spotted a Bumblebee Hummingbird in the wild? Share your experiences in the comments below! For more information about the world of birds, check out our newsletter on avian species and their unique traits.
Read also :
An Invitation to Nature: The Bird Feeder